What is Form 8809?
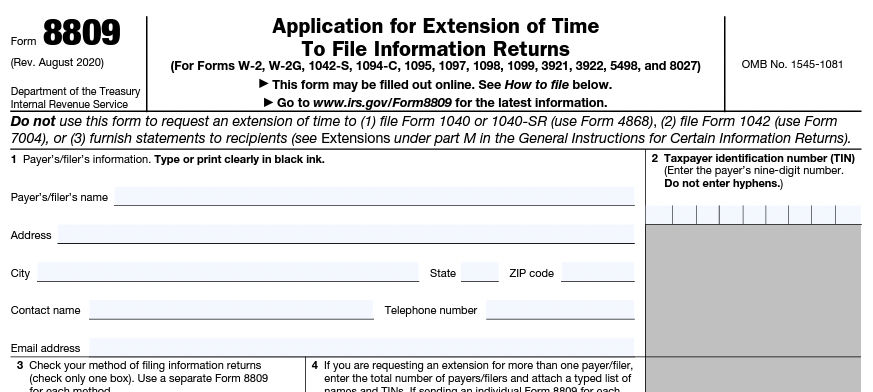
Form 8809 is an IRS form titled "Application for Extension of Time to File Information Returns." It is used by individuals or companies in the United States who need additional time to submit certain information returns, such as:
-
Form W-2, Wage and Tax Statement
-
Form W-2G, Certain Gambling Winnings
-
Form 1042-S, Foreign Person's U.S. Source Income Subject to Withholding
-
Form 1094-C, Transmittal of Employer-Provided Health Insurance Offer and Coverage Information Returns
-
Form 1095 series (such as 1095-A, 1095-B, and 1095-C)
-
Form 1097, BTEC (Bond Tax Equity Credit) Payment
-
Form 1098 series (such as Form 1098, Mortgage Interest Statement; - Form 1098-E, Student Loan Interest Statement; and Form 1098-T, Tuition Statement)
-
Form 1099 series (such as 1099-MISC, 1099-INT, 1099-DIV, etc.)
-
Form 3921, Exercise of an Incentive Stock Option Under Section 422(b)
-
Form 3922, Transfer of Stock Acquired Through an Employee Stock Purchase Plan Under Section 423(c)
-
Form 5498 series (such as 5498-SA and 5498-ESA)
-
Form 8027, Employer's Annual Information Return of Tip Income and Allocated Tips
The form allows filers to request a 30-day extension of time to file beyond the original due date for submitting these information returns. It's important to note that Form 8809 is for an extension of time to file the returns, not an extension of time to pay any taxes due.
To request an extension, filers must complete Form 8809, providing information such as their name, address, social security number (SSN) or taxpayer identification number (TIN), and the type of return for which they are requesting an extension. The form should be submitted to the IRS before the due date of the information returns for which you are requesting an extension. Keep in mind that the IRS has the right to deny the extension request if it is not filed in a timely manner or if the filer has a history of not complying with filing requirements.
Who needs to file Form 8809?
Businesses, organizations, or individuals who are required to file certain information returns and need additional time to prepare and submit those returns can use Form 8809. Here are some examples of entities that may need to file Form 8809:
-
Employers who need extra time to file Form W-2: If an employer is unable to prepare and submit all Forms W-2 for their employees by the original due date (usually January 31st), they can use Form 8809 to request a 30-day extension.
-
Payers of miscellaneous income who need extra time to file Form 1099: If a business or individual who has paid non-employee compensation, interest, dividends, or other reportable payments cannot submit all required Forms 1099 by the original due date (usually January 31st for non-employee compensation and February 28th for other types of income), they can request an extension using Form 8809.
-
Financial institutions or educational institutions who need extra time to file Forms 1098: If these entities are unable to file forms like Form 1098 (mortgage interest), Form 1098-T (tuition and related expenses), or Form 1098-E (student loan interest) by the original due date (usually February 28th), they can use Form 8809 to request an extension.
-
Financial institutions or plan administrators who need extra time to file Form 5498: If these entities cannot are unable to file tax forms related to IRA contributions, rollovers, or other tax-favored savings accounts by the original due date (generally May 31st), they can request an extension using Form 8809.
Filers seeking an extension of time to file should complete and submit Form 8809 on or before the original due date of the information returns they are responsible for. Form 8809 should include the filer’s name, address, and taxpayer identification number, as well as the type of return for which they are requesting an extension.
It's crucial to remember that Form 8809 only grants an extension of time to file the returns, and it does not grant an extension of time to pay any taxes due. As a result, filers of information returns who owe taxes should ensure they pay any taxes owed by the original due date.
Who is not required to file Form 8809?
Entities or individuals who are not required to file Form 8809 include those who:
-
Are not responsible for filing information returns: If you are not an employer, payer of miscellaneous income, financial institution, educational institution, or plan administrator that needs to file information returns (e.g., Forms W-2, 1099, 1098, or 5498 series), you do not need to file Form 8809.
-
Will file information returns on time: If you plan to prepare and submit your required information returns by the original due date, you do not need to file Form 8809.
-
Are seeking an extension for filing individual or business income tax returns: Form 8809 is specifically for requesting extensions on information returns, not income tax returns. If you need an extension to file your individual income tax return, use Form 4868, "Application for Automatic Extension of Time to File U.S. Individual Income Tax Return." For business income tax returns, use Form 7004, "Application for Automatic Extension of Time to File Certain Business Income Tax, Information, and Other Returns."
Remember, Form 8809 is solely for requesting extensions on certain information returns. If you do not fall into the categories of filers responsible for submitting those returns or can file them on time, you are not required to file Form 8809.
When is the deadline for Form 8809?
The deadline for filing Form 8809, "Application for Extension of Time to File Information Returns," is the original due date of the information returns for which you are requesting an extension. Here are some common information return due dates:
-
Form W-2: The deadline for submitting Form W-2 to the Social Security Administration is typically January 31st. Therefore, to request an extension, you should submit Form 8809 by January 31st.
-
Form 1099 series: For most types of 1099 forms, the deadline for submitting to the IRS is February 28th if filing on paper or March 31st if filing electronically. However, Form 1099-NEC (Nonemployee Compensation) has a due date of January 31st.
-
Form 1098 series: The deadline for submitting Form 1098, Form 1098-T, and Form 1098-E is generally February 28th if filing on paper or March 31st if filing electronically. To request an extension, submit Form 8809 by the applicable due date.
-
Form 5498 series: The deadline for submitting Form 5498 is typically May 31st. To request an extension, submit Form 8809 by May 31st.
Note that while the due date for these forms can be extended, you’ll still need to provide copies of all information returns to recipients. The due date to send copies to recipients is generally January 31st of each year (with the exception of Forms 1099-B, 1099-S, and any Forms 1099-MISC containing data in boxes 8 or 10).
Can the deadline for Form 8809 be extended?
The deadline for filing Form 8809 cannot be extended beyond the original due date of the information returns for which you are requesting an extension. Form 8809 must be submitted by the original due date of the specific information return you need an extension for, such as Form W-2, Forms 1099, Form 1098, or Forms 5498.
When you file Form 8809 on or before the original due date, the IRS will grant a 30-day extension for filing the information returns if the extension request is approved. However, there is no provision to request additional time to submit Form 8809 itself.
To avoid penalties and ensure your extension request is processed, it is crucial to submit Form 8809 by the applicable deadline for the specific information return you are responsible for filing.
What is the penalty for late filing of Form 8809?
Form 8809 itself does not have a penalty for late filing. However, if you fail to submit Form 8809 by the original due date of the information returns for which you are requesting an extension, your extension request may be denied by the IRS. In this case, you may be subject to penalties for late filing of the actual information returns.
The penalties for late filing of information returns can vary depending on the type of return and how late it is filed. Some of the general penalties for late filing of information returns include:
-
A penalty of $50 per return if you file the return within 30 days after the due date, with a maximum penalty of $220,500 per year ($630,500 for larger businesses).
-
A penalty of $110 per return if you file the return more than 30 days after the due date but by August 1, with a maximum penalty of $630,500 per year ($1,891,500 for larger businesses).
-
A penalty of $290 per return if you file the return after August 1 or not at all, with a maximum penalty of $1,261,000 per year ($3,783,000 for larger businesses).
-
A penalty of $580 per return if you intentionally disregard filing the return, with no maximum penalty.
Note that the IRS may reduce the penalties or waive them entirely if you can show reasonable cause for late filing.
It's important to submit Form 8809 by the original due date of the information returns to avoid the risk of being subject to penalties for late filing of those returns. If you are unsure about deadlines or penalties, consult a tax professional for guidance.
What happens if I don't file Form 8809?
If you don't file Form 8809 and fail to submit your information returns (such as Forms W-2, 1099, 1098, or 5498) by their original due date, you may face potentially significant penalties for late filing of those returns.
Not filing Form 8809 when you need an extension may result in the following consequences:
-
Late filing penalties: As mentioned earlier, the IRS imposes penalties on late filing of information returns, which vary depending on how late the returns are filed. The penalties can range from $50 to $290 per return, with maximum annual penalties based on the size of your business. If you neglect to file the returns intentionally (“intentional disregard”), then the penalties can be much higher.
-
Compounding penalties: The longer you delay submitting your information returns, the higher the penalties may become. The penalties may continue to accrue until the required information returns are filed.
-
Potential issues for recipients: Late filing of information returns like Forms W-2, 1099, or 1098 can cause issues for the recipients of those forms. They may have difficulty filing their own tax returns on time, which could lead to additional complications and potential penalties for them as well. They may seek to pursue legal action against you if you neglect to provide them with these forms.
What supporting documents do I need to file with Form 8809?
When filing Form 8809, "Application for Extension of Time to File Information Returns," you generally do not need to provide any additional supporting documents. The form itself is designed to be simple and straightforward. You are required to provide the following information:
-
Your name, address, and phone number (or that of your business).
-
Your taxpayer identification number (TIN), which can be your Social Security number (SSN), Employer Identification Number (EIN), or Individual Taxpayer Identification Number (ITIN), depending on your situation.
-
The type of information return you need an extension for, such as Form W-2, 1099 series, 1098 series, or 5498 series.
-
The reason for requesting the extension (if you are requesting an extension for more than one type of form or a second extension).
In most cases, the IRS does not require any additional documentation or explanations for granting the initial 30-day extension. However, they may request additional information in specific situations, such as if they need to verify the information provided on the form.
We recommend keeping a record of the information used in preparing the forms, such as the recipient’s name, address, Taxpayer Identification Number (TIN), and any records of payment amounts, taxes withheld, etc. This will allow you to be prepared if the IRS ever requests additional information related to the forms.
How do I file Form 8809?
To file Form 8809, "Application for Extension of Time to File Information Returns," you can choose to file either electronically, by mail, or by hiring a tax professional, depending on your preference and the type of information returns you need to file. Here's how to file Form 8809:
-
Collect all information related to the form: Your name, address, phone number, TIN, the type of information return you’re requesting an extension for, and the reason for the extension request.
-
Obtain the form:
-
If you’re paper filing: Download a copy of Form 8809 from the IRS website. You can also obtain a copy from your tax professional or by contacting the IRS.
-
If you’re filing electronically: Access the IRS’s “Filing Information Returns Electronically” (FIRE) system, log in or create an account, and follow the prompts to file your information return(s) electronically.
-
If you’re hiring a tax professional: find a trusted tax professional or tax firm in your area. Discuss your needs with them, and they’ll file Form 8809 on your behalf.
-
-
Complete the form: Fill out the required information, including your name, address, phone number, taxpayer identification number (TIN), the type of information return for which you are requesting an extension, and the reason for the extension (if applicable).
-
Choose a filing method: Once you understand the requirements for Form 8809 and have collected all the necessary information, it’s time to choose your filing method: paper, electronic, or tax professional.
-
Submit the form: Ensure that you file Form 8809 by the original due date of the information returns for which you are requesting an extension. The IRS will review your request and notify you if the extension is granted or denied.
Where should I mail Form 8809 to?
If you decide to file Form 8809 by paper, the IRS provides the following mailing address:
Department of the Treasury
Internal Revenue Service Center
Ogden, UT 84201-0209
Be sure to check the IRS website and/or the Form 8809 Instructions (located below the actual form) if you’d like to double check the address or any other filing requirements.
You must mail Form 8809 by the original due date of the information returns for which you are requesting an extension. Keep in mind that you also have the option to file Form 8809 electronically through the IRS's Filing Information Returns Electronically (FIRE) system.
Can I file Form 8809 electronically?
Yes, you can file Form 8809, "Application for Extension of Time to File Information Returns," electronically using the IRS's Filing Information Returns Electronically (FIRE) system. Here's how to file Form 8809 electronically:
-
Access the FIRE system: Go to the FIRE system website and log in. If you are a first-time user, you will need to create an account by clicking on "Create New Account" and following the registration process.
-
Prepare your form: The FIRE system requires you to submit your Form 8809 information in a specific electronic format. You can find the required format and instructions in the IRS Publication 1220, "Specifications for Electronic Filing of Forms 1097, 1098, 1099, 3921, 3922, 5498, and W-2G." The publication is available on the IRS website at https://www.irs.gov/pub/irs-pdf/p1220.pdf.
-
Once you’re logged in, upload your file: Once you have prepared your Form 8809 information in the required electronic format, log into the FIRE system, select "Send Information Returns" from the main menu, and follow the on-screen instructions to upload your file.
-
Receive confirmation: After successfully submitting your Form 8809, the FIRE system will provide a confirmation message. Make sure to keep a record of this confirmation for your records.
Ensure that you submit Form 8809 electronically by the original due date of the information returns for which you are requesting an extension. If you prefer to file by mail, you can also send a paper copy of Form 8809 to the appropriate IRS address mentioned in the form's instructions.
In the case you need to produce payslips for your workers or permanent employees, you can always try out this instant paystub maker.