What Is Form 1040?
Form 1040, U.S. Individual Income Tax Return, is the IRS tax form filed by taxpayers classified as individuals in the United States.
Useful Information
Form 1040, U.S. Individual Income Tax Return, is the IRS tax form filed by taxpayers classified as individuals in the United States.
Depending on your tax situation, you may have to submit supplemental IRS tax forms with your Form 1040.
An income tax filer in the United States who meets the definition of an individual in the eyes of the IRS must complete a Form 1040. There are very few exceptions to the requirement to file a tax return. If you are claimed as a dependent on someone else's tax return, you do not have to file your own tax return. If you receive Social Security benefits and have no other income, you do not have to file a tax return.
If you need to prove your income, you may also want to check out our paystub generator online as we’ve got diverse paystubs templates for you to choose from.
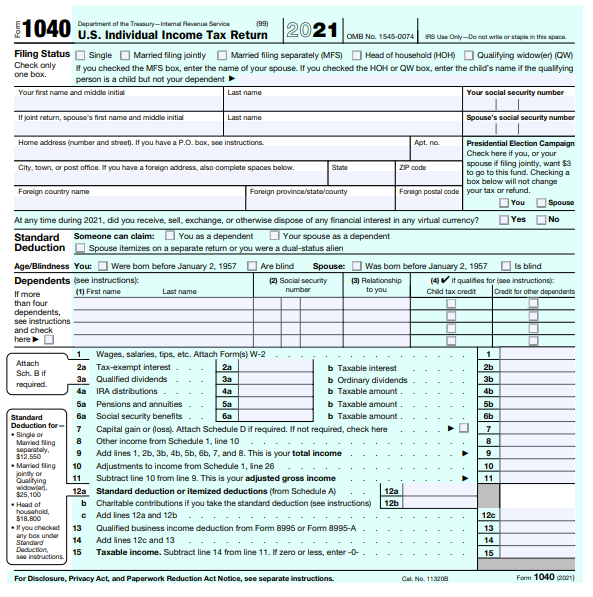
You will need to know your social security number, filing status, and relevant information for your spouse and any dependents you plan to claim. You will also need to have tax documents on hand that support your earned income and provide validity to any deductions or credits you are claiming.
If you receive employee wages paid by a business, your employer will provide you with a Form W-2, Wage and Tax Statement around the end of January before tax filing season. The Form W-2 lists your income from your employment as well as your income taxes that were withheld by your employer on your behalf throughout the tax year. It will be used to calculate your total taxable income on your tax return.
If you work an independent contractor, it is your responsibility to track and pay self-employment taxes and income taxes on your own earnings. You will typically receive a Form 1099-NEC, Non-Employee Compensation, from businesses you received payments from throughout the previous year. These 1099-NEC(s) should be received around the end of January.
If you own a home with a mortgage, your mortgage lender will send you a Form 1098, Mortgage Interest Statement, detailing your mortgage interest, mortgage insurance premiums, and any points paid on your principal residence. This information can be used if you itemized deductions.
Other important documents to keep an eye out for include the common 1099 series forms. These forms will come from the respective payers.
Your income tax return will report all the information necessary to identify your total taxable income and total federal income tax. The top section is where you'll input your personal information such as your filing status, name, social security number, and address. You will also need to enter the same information for your spouse and any dependents you are claiming on your income tax return.
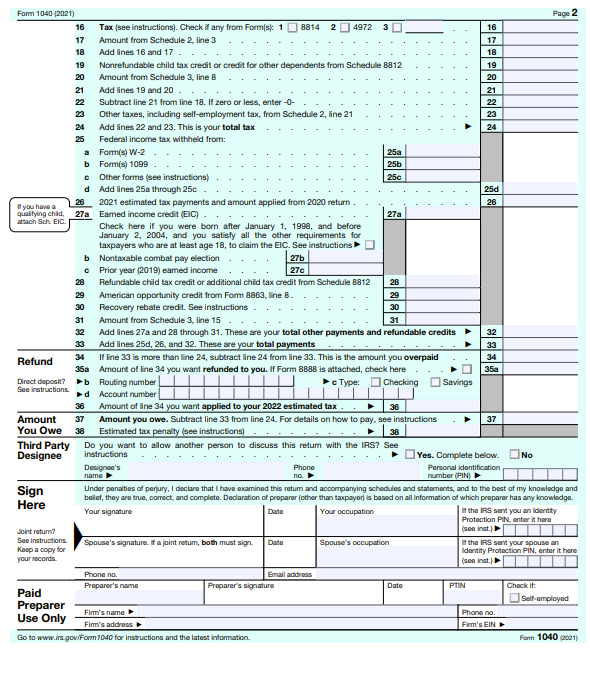
The first 15 lines of the income tax return include all sources of income and deductions that are used to arrive at your total taxable income. Lines 16 to 24 show your income tax liability and certain tax credits to arrive at your total federal income tax. Lines 25 through 33 show your federal income taxes already paid through withholdings or estimated tax payments and refundable tax credits, such as the earned income credit.
If your federal income taxes paid are greater than your total tax, you are due a refund. Your refund will appear on line 34. Line 35 is where you include your banking information if you want your tax refund direct deposited in your account, and line 36 gives you the option to apply some of your refund to your next year's income tax return. If you have not paid enough in income taxes throughout the year, line 37 is the amount you still owe on your federal income tax. If you have an amount in line 37, line 38 calculates an estimated tax penalty.
The bottom section is where you, and your spouse if applicable, sign that the information is complete to the best of your knowledge. If you used a paid preparer, their information goes in the very last section.
There are several forms of income that are commonly referred to by tax professionals when discussing your income tax return. Here are the most common.
Tax deductions reduce your adjusted gross income to arrive at your total taxable income. It effectively reduces your income tax liability by the amount of your marginal tax rate.
If you choose to itemize deductions, these are some of the most common deductions available to you.
Here are some above-the-line deductions that you can qualify for even if you take the standard deduction:
Tax credits reduce your income tax liability dollar for dollar. If you owed $5,000 in income tax before your $2,000 tax credit, you will now owe $3,000. As such, they are even more beneficial than tax deductions.
Certain tax credits are "refundable," meaning you can receive the amount of the credit paid to you even if you do not owe that much in taxes. Nonrefundable tax credits, on the other hand, only reduce your tax liability to zero. If any credit remains, you forfeit the additional credit amount.
Here are some of the most common refundable tax credits.
Here are some of the most common non-refundable tax credits you can utilize to reduce your total income tax liability.
The deadline for filing your Form 1040 income tax return is typically April 15 of the year following the tax year in question. If April 15 falls on a weekend, the deadline is generally extended to the following Monday.
Yes, you can file an extension of time to file your income tax return. The extension is good for six additional months, generally bringing the deadline to October 15.
It is important to note that an extension of your time to file your income tax return does not automatically extend your time to pay your taxes. You should be certain that your federal income tax has been paid in full if you decide to extend your income tax return filing deadline, or you will be subject to penalties and interest charges.
Yes, there is a penalty for late filing your income tax return. The failure to file penalty is 5% of your unpaid taxes each month you fail to file your income tax return, capping out at 25% of your unpaid taxes. If the return is over 60 days late, the minimum failure to file penalty is $435 as of 2022. The IRS also charges interest on penalties.
Where your income is reported on the Form 1040 depends on whether you are considered an employee or an independent contractor.
If you receive income under a traditional form of employment where you work for another employer, your wages will appear on Line 1 of the Form 1040.
As an independent contractor or freelancer, your earnings will appear on a different line than someone receiving payments from an employer. Rather than being entered directly on Form 1040 like wages from employment, it will flow through to the Form 1040 from accompanying schedules.
If you claim certain tax credits, such as the earned income credit or the additional child tax credit, it may slow down your tax refund as well.
Your tax filing status affects your ordinary income tax bracket and ability to access certain tax credits, such as the earned income credit. Your filing status is determined based on whether you are married or unmarried. The answer to that question on the last day of the year determines your tax filing status for the entire tax year.
There are exceptions to the general rule. If your spouse passed away within the previous tax year, you are considered a qualifying widow(er) and can file married filing jointly for the tax year of your spouse's death. Additionally, if you are single and have dependents, you may qualify for the more beneficial tax filing status, head of household.
Taxpayers who file a joint tax return with a spouse generally receive the greatest tax benefits. If you file a joint tax return, your filing status qualifies you for many beneficial tax credits and the standard deduction is double that of a single taxpayer.
Married filing separately is generally considered to be the least beneficial tax filing status. This filing status does not qualify for many tax credits, including the earned income credit, American opportunity credit, and lifetime learning credit. You will also lose access to the student loan interest deduction, and your standard deduction will be half that of taxpayers filing a joint tax return.
Head of household is a beneficial tax filing status for single taxpayers who have dependents and pay for more than half the costs of a home. The qualifying dependent does not have to be a child of the taxpayer. It comes with the benefit of a higher standard deduction (although it's lower than married filing jointly) and higher income thresholds on the ordinary income tax brackets, effectively lowering your tax bracket.
Single filers have a standard deduction that is half that of married filing jointly, but you do qualify for all the same tax credits under this filing status.
Whether you should take the standard deduction or itemize your deductions depends on which method arrives at the larger amount for your particular tax situation. It is always beneficial to add up all your potential itemized deductions to compare to the standard deduction for your filing status.
The standard deduction for 2022 is:
You can take the qualified business income deduction even if you take the standard deduction. The qualified business income deduction allows a self-employed income tax filer to deduct up to 20% of their qualified business income on their income taxes.
Additionally, in recent years, you can take up to a $300 charitable contribution deduction ($600 for married filing jointly) in addition to the standard deduction.
Common itemized deductions include home mortgage interest, home equity loan interest (if the loan was used to substantially improve upon the home secured by the loan), local property taxes, and unreimbursed medical and dental expenses that exceed 7.5% of your adjusted gross income. If you have large expenses in these areas, it may make sense to itemize your deductions.
Need Help? Chat with us and we'll help you fill the form.
Brett Hello! Don't hesitate to reach out if you have any questions. I'm just a message away!
We respond immediately