Form 1040 Schedule SE Generator
What is the Schedule SE?
Schedule SE, the Self Employment Tax Form, is a tax form used by the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) to determine and report the taxes due on the self-employment income of individuals who are self-employed or run their own business. The self-employment income reported on Schedule SE includes both income earned from operating a business as a sole proprietor, as well as income earned from providing services as an independent contractor. Often, this income will be carried over to Schedule SE from other tax forms, such as Schedule C (Profit or Loss From Business).
Once all self-employment income has been added up, Schedule SE is used to calculate the self-employment tax, which is the equivalent of the Social Security and Medicare taxes that are usually withheld from an employee's wages. The total self-employment tax calculated on Schedule SE will be carried to Schedule 2, Line 4, and will then be included in “Total Other Taxes” on Form 1040, Line 23.
What information does Schedule SE include?
Schedule SE includes various types of information related to an individual's self-employment income and taxes. This includes:
-
Total self-employment income earned, including income from any business activities or services provided as an independent contractor.
-
Because Schedule SE includes net profits from other forms (such as Schedule C), it automatically takes into account business expenses and any deductions and credits that the taxpayer may be eligible for.
-
Calculations for self-employment tax, which is calculated on Schedule SE and is then added to regular income taxes on page 2 of Form 1040, U.S. Individual Income Tax Return.
-
Personal information, such as the name and social security number of the taxpayer.
What types of income does Schedule SE cover?
Schedule SE covers income from self-employment or business activities, such as freelance work, consulting, or running a small business. It also covers income from any services provided as an independent contractor. Self-employment income is defined as any income earned from a trade or business that an individual operates as a sole proprietor or as an independent contractor.
This generally includes the income you earn from sources other than wages, salaries, tips, or investing. Examples include income earned from providing services as a freelance writer, graphic designer, consultant, or running a small business, like a retail store or a restaurant. It does not cover wages earned as an employee, salaries, tips, investment income, and other forms of compensation.
Who needs to file Schedule SE?

Schedule SE, also known as the "Self-Employment Tax” Form, is used by individuals who are self-employed and have net earnings of $400 or more from their self-employment activities. This form is used to calculate the individual's self-employment tax, which is the equivalent of the Social Security and Medicare taxes that are typically withheld from an employee's wages by an employer. If an individual meets the criteria for filing Schedule SE, they must file the form as part of their annual federal Form 1040 Individual Income Tax Return.
Which taxpayers are required to file Schedule SE?
Taxpayers who are self-employed and have net earnings of $400 or more from their self-employment activities are eligible to file the Schedule SE. This includes individuals who own a business, are an independent contractor, are a partner in a partnership, or are a member of a limited liability company (LLC) that is treated as a partnership for tax purposes.
Additionally, if you are considered a statutory employee and you received a W-2 form with box 13, "Statutory employee" checked and if you are a church employee, you are required to file Schedule SE and calculate self-employment taxes.
What are the exemptions and exclusions of the Schedule SE?
Schedule SE calculates self-employment tax, which is the equivalent of the Social Security and Medicare taxes that are typically withheld from an employee's wages by an employer. However, there are certain exemptions and exclusions that may apply to reduce or eliminate the self-employment tax that an individual is required to pay.
Some of the exemptions and exclusions of Schedule SE are:
-
Certain income derived from farming or fishing can be exempt from self-employment tax.
-
Income earned by a limited partner in a partnership is not subject to self-employment tax.
-
Certain income earned by a member of a limited liability company (LLC) may be exempt from self-employment tax, depending on the member's level of involvement in the LLC's business operations.
-
Income earned by a real estate agent or direct seller may be eligible for exclusion from self-employment tax.
-
Certain clergy members may be able to exclude a portion of their income from self-employment tax.
When is the deadline to file a Schedule SE?
Schedule SE is filed along with your Form 1040, U.S. Individual Income Tax Return. The deadline to file both of these forms is typically April 15th of each year. If April 15th falls on a weekend or holiday, the deadline is extended to the next business day.
It's also important to note that self-employed individuals with net income are generally required to make estimated tax payments throughout the year, rather than just paying taxes once per year on April 15th. If you expect to owe more than $1,000 in taxes for the year and you did not have taxes withheld from your income, you will need to make quarterly estimated tax payments. The due dates for these payments are typically April 15th, June 15th, and September 15th of the current tax year, and January 15th of the following tax year.
What are the differences between Schedule SE and the Form 1040?
Purpose: Schedule SE is used by self-employed individuals to calculate their self-employment tax, which is the equivalent of the Social Security and Medicare taxes that are typically withheld from an employee's wages by an employer. Form 1040 is used by all individual taxpayers to report their taxable income and calculate their federal income tax liability.
Who must file: Any individual with net earnings of $400 or more from self-employment activities is required to file Schedule SE. To file Form 1040, an individual must have taxable income above certain thresholds, defined by that tax year’s standard deduction amount.
Formulas: Schedule SE uses a specific formula to calculate self-employment tax, which is based on the individual's net self-employment income. Form 1040 uses a progressive tax rate structure to calculate the taxpayer’s federal income tax liability, which is based on the individual's taxable income. If you need to produce paystubs to prove that you earn income as a self-employed individual, be sure to check out the instant paystub generator.
Additional forms: When filing Schedule SE, you must also file Form 1040 and attach Schedule SE to it. Form 1040 does not require additional forms to be filed with it, but certain individuals may need to attach other forms (such as a Schedule C or Schedule E) to report specific types of income, expenses, or deductions.
Deadline: The deadline to file Schedule SE, along with your personal income tax return, is typically April 15th of each year. If April 15th falls on a weekend or holiday, the deadline is extended to the next business day.
What documents do I need to have on hand to fill out Schedule SE?
When filling out Schedule C, Profit or Loss From Business, And Schedule SE, Self-Employment Tax Form, you will need to have certain documents and information on hand in order to accurately report your income and expenses and calculate your self-employment tax. Some of the documents you may need include:
-
Records of income: You will need to have records of all income received from self-employment activities, such as invoices, receipts, and/or bank statements.
-
Records of expenses: You will need to have records of all expenses related to your self-employment activities, such as receipts, invoices, and bank statements for items like office supplies, equipment, and travel, among other categories.
-
Social security number: You will need to have your Social Security number or Employer Identification Number (EIN) in order to file Schedule SE.
-
Business income schedules: You will need to fill out Schedule C, Schedule C-EZ, or Schedule F, depending on the type of business you have. These forms are used to report your business income and expenses.
-
Form 1099-MISC: If you received Forms 1099-MISC, which report payments of non-employee compensation of $600 or more, you'll need to include that income on your Schedule C or C-EZ.
-
Schedule SE: This form is used to calculate your self-employment tax, using the information from your Schedule C, Schedule C-EZ, or Schedule F.
How do I calculate my self-employment tax using Schedule SE?
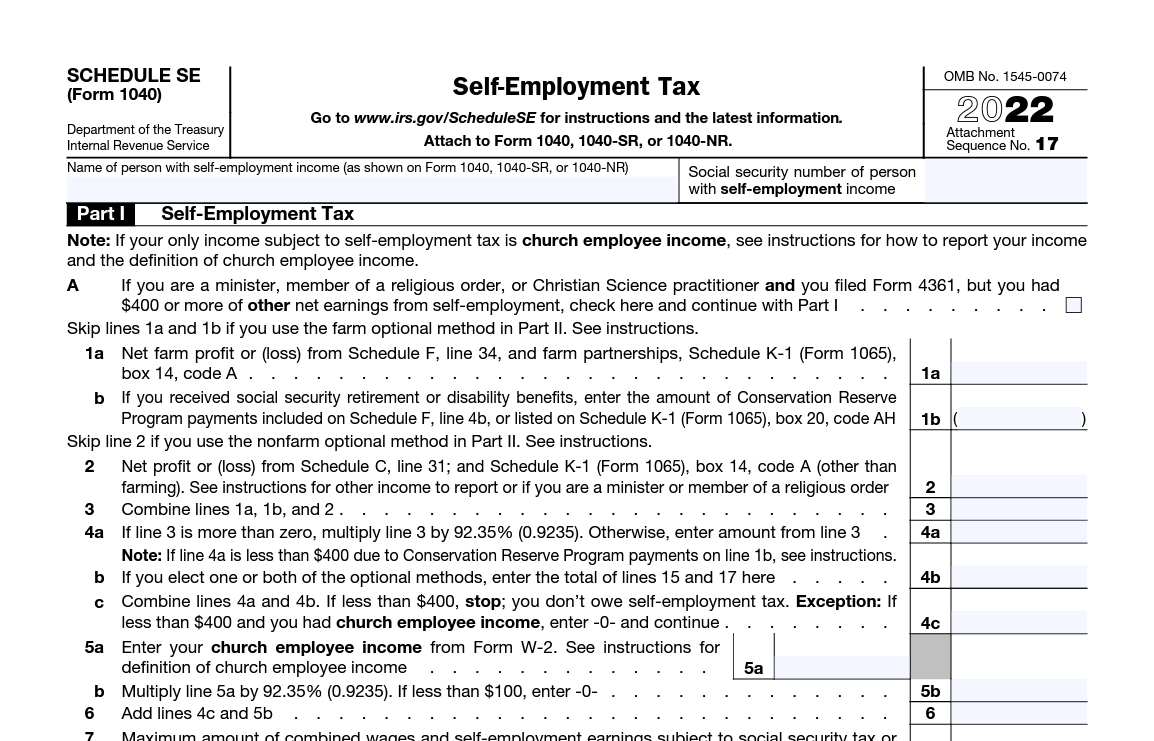
Schedule SE is used to calculate your self-employment tax, which is the equivalent of the Social Security and Medicare taxes that are typically withheld from an employee's wages by an employer. The form walks you through the process, and the formula for calculating your self-employment tax is as follows:
-
Determine your net self-employment income: This is calculated by subtracting your business expenses from your gross self-employment income. Your gross self-employment income would include any money you earned as an independent contractor or from your own business, and any income earned as a partner in a partnership.
-
Multiply your net self-employment income by 92.35%. The resulting amount is subject to self-employment tax.
-
Multiply the amount subject to self-employment tax by the current self-employment tax rate. For tax years 2021 and 2022, the self-employment tax rate is 15.3% (12.4% for Social Security and 2.9% for Medicare). For 2021, the first $142,800 of self-employment income is taxable. For 2022, that limit is increased to $147,000.
-
Calculate the self-employment tax credit by using Schedule SE (Form 1040).
For more information, check out the official Schedule SE form here, or read the IRS’s Schedule SE instructions here.
What happens if I make a mistake on my Schedule SE?
If you make a mistake on your Schedule SE, it's important to correct it as soon as possible to avoid potential penalties and interest charges. There are a few different ways to correct a mistake on your tax return, depending on the nature of the error and the stage of the tax-filing process.
-
Amending a return: If you have already filed your tax return and you need to correct errors or make changes, you can file an amended return using Form 1040X, Amended U.S. Individual Income Tax Return. Keep in mind that you will have to file the form within three years of the original tax return's due date, but you should file it as early as possible to avoid issues with the IRS.
-
Wait for the IRS to contact you: if the error is small or does not result in a change to taxable income or taxes owed/refunds received, then the IRS may do nothing. If they do contact you (they will mail you a letter), they will state the nature of the error and give you the opportunity to either respond to their letter or file an amended tax return.
-
Sending a letter to the IRS: If you made a small error on your return, such as a minor math mistake, you can send a letter to the IRS explaining the error, along with any corrected forms or schedules. They may or may not respond with instructions, depending on the nature and scale of the error.
It's important to keep in mind that if you owe additional taxes or additional self-employment tax as a result of a mistake on your return, you'll need to pay the additional taxes to avoid any penalties and interest.
What are the consequences of not correcting a mistake on my Schedule SE?
Not correcting a mistake on your Schedule SE can have several consequences, including:
-
Underpaying taxes: If you under report your income or overstate your deductions on your Schedule SE or Form 1040, you may owe additional taxes, and possibly penalties and interest charges.
-
Overpaying taxes: If you over report your income or understate your deductions on your Schedule SE or Form 1040, you may be entitled to a refund, but you will have to file an amended return and claim the refund.
-
Penalties: The IRS may impose penalties for underreporting income, failing to file a return, or failing to pay taxes on time. These penalties can be substantial and can add up quickly.
-
Interest: The IRS may charge interest on any taxes that are not paid on time. The interest rate can change quarterly and it can be substantial.
-
Criminal charges: In some cases, failure to file a tax return or failure to pay taxes can result in criminal charges and prosecution.
-
No response: if the error is very minor and does not affect taxable income, tax owed, or your refund received, then the IRS may choose to do nothing.
It's important to keep in mind that the sooner you correct a mistake on your tax return, the less likely you are to face penalties and interest charges. We recommend consulting a tax professional or referring to the IRS website for information on how to correct mistakes on your tax return and understand any potential penalties and interest charges that may apply.
Can I e-file my Schedule SE or do I have to mail it?
Yes, you can e-file your Schedule SE along with your regular Form 1040. In fact, electronically filing is becoming the most common method of filing taxes as it saves time and reduces the risk of errors. Additionally, e-filing makes it easier to track the status of your return, and you will usually receive your refund faster if you e-file.
To e-file your Schedule SE, you can either use tax preparation software or the IRS’s e-file system. You can also use the services of a tax professional, who can e-file your tax return for you.
It's important to note that, before you e-file, you should double-check the accuracy of your return and make sure you have all the necessary forms and documentation. Also, If you are e-filing, you'll need to provide your bank account information so that the IRS can direct deposit your refund.
You can also mail your Schedule SE along with Form 1040, but it may take longer to process and you will not be able to track the status of your return.
How Do I File Schedule SE?
To file Schedule SE, you will need to gather information about your income and expenses related to your self-employment. This includes income from freelance or contract work, as well as expenses related to running your business, such as office expenses and supplies. This information will be included on Schedule C, Schedule E, and other locations on your Form 1040 tax return, and will then be carried over to Schedule SE.
Once these schedules are properly filled out, Schedule SE will be attached to your Form 1040 and they will be filed together. You can file Form 1040 and Schedule SE electronically using the IRS’s e-file system, or by mailing in a paper copy. In order to e-file, you will need to have a Self-Select PIN using an online filing resource, or contact a tax professional authorized to have them e-file on your behalf.
If you’d like to mail your Form 1040, the address will depend on your individual circumstances and where you live. The most common addresses for mailing Form 1040 and the accompanying Schedule SE are:
| If you live in... | And you are not enclosing a payment, use this address | and you are enclosing a payment, use this address |
| Arkansas ,Connecticut, Delaware, District of Columbia, Illinois, Indiana, Iowa, Kentucky, Maine, Maryland, Massachusetts, Minnesota, Missouri, New Hampshire, New Jersey, New York, Oklahoma, Rhode Island, Vermont, Virginia, West Virginia, Wisconsin | Department of the Treasury Internal Revenue Service Kansas City, MO 64999-0002 | Internal Revenue Service P.O. Box 931000 Louisville, KY 40293-1000 |
| Pennsylvania | Department of the Treasury Internal Revenue Service Kansas City, MO 64999-0002 | Internal Revenue Service P. O. Box 802501 Cincinnati, OH 45280-2501 |
| Florida, Louisiana, Mississippi, Texas | Department of the Treasury Internal Revenue Service Austin, TX 73301-0002 | Internal Revenue Service P.O. Box 1214 Charlotte, NC 28201-1214 |
| Alabama, Georgia, North Carolina, South Carolina, Tennessee | Department of the Treasury Internal Revenue Service Kansas City, MO 64999-0002 | Internal Revenue Service P O Box 1214, Charlotte, NC 28201-1214 |
| Arizona, New Mexico
| Department of the Treasury Internal Revenue Service Austin, TX 73301-0002 | Internal Revenue Service P.O. Box 802501, Cincinnati, OH 45280-2501 |
| Alaska, California, Colorado, Hawaii, Idaho, Kansas, Michigan, Montana, Nebraska, Nevada, Ohio, Oregon, North Dakota, South Dakota, Utah, Washington, Wyoming | Department of the Treasury Internal Revenue Service Ogden, UT 84201-0002 | Internal Revenue Service P.O. Box 80250, Cincinnati, OH 45280-2501 |
Always be sure to check the IRS website for the most recent and updated mailing addresses and any special instructions regarding mailing your return. It's also important to note that if you owe taxes and you're mailing your return, you should send your payment (via check, not cash) along with your tax return to the appropriate address.