What Are The 4 Main Types Of Taxes?
Taxes are a fact of life, and we all pay them, so it is a good idea to understand what they are and why they are levied. We are going to answer the question ‘what are the 4 main types of taxes’ as they relate to income to help you understand this subject.
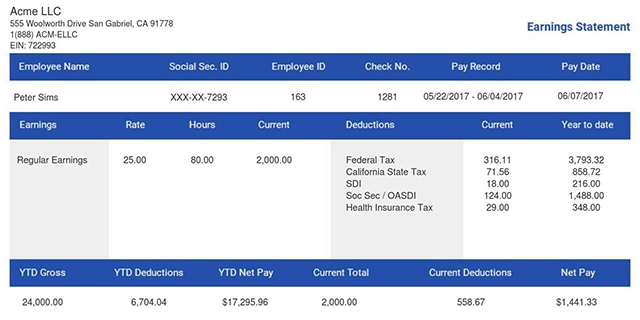
Also read: How to Review Your Paychecks Before Filing Income Taxes

Income Tax
Income tax stems from the generation of revenue through a job or personal venture. It can also come from interest income. By law all taxpayers must file a tax return every year in order to pay the tax due on their income.
The federal government raises a lot of revenue from income tax and 41 states also levy tax on income. Some counties and cities also impose an income tax.
The federal tax rates range from 10% to 37% but county and city income tax rates are typically lower ranging from 0% to just over 13% in California. The revenue from income tax is used to fund public services, and to pay government obligations.
These include Social Security, Medicare, national defense and security as well as interest on the national debt.
Income tax was first introduced by Abraham Lincoln in 1862 as a way of paying for the military expenses of the Civil War but only for a period of 10 years. However, it was revived by William H. Taft as a way of reducing the government reliance on trade tariffs for revenue.
In July 1909 the 16th Amendment to the Constitution was passed and allowed the federal government to collect income tax. Americans have been paying income tax ever since.
Businesses also pay income tax and this applies to small businesses, self-employed workers, partnerships and corporations.
Also read: A Full Guide on How to Calculate Income Tax On A Pay Check

Payroll Tax
Payroll taxes are deducted directly from a worker’s paycheck and consists of two different percentages. The first is to fund Social Security and this is set at 7.65%. The other funds Medicare and is payable at 1.45%.
There is an income cap of $147,000 on the amount at which employees contribute to the Social Security fund. This is a regressive tax, meaning the amount decreases as earnings rise, having the effect that lower earners pay a higher percentage.
Medicare contributions do not have an income cap but those earning over $200,000 pay an extra 09% for Medicare.
Employees pay into these funds during their working years so that if after retirement they need to use these services they will have contributed to them.
The portion that covers Social Security is simply labeled FICA while the percentage levied for Medicare is labeled MedFICA on pay stubs.
As well as being deducted from employees’ paychecks an employer is required to match these amounts. Their deductions as well as the employees’ are then paid by the employer to the federal government.
Payroll taxes are payable on wages, salaries and tips. It is used to cover Social Security and Medicare contributions as well as federal, state and local income taxes. The Federal Insurance Contributions Act or FICA mandates this tax.
Also read: Mandatory Deductions From Your Paycheck
Capital Gains Tax
A capital gains tax is imposed on any profits which are earned following the sale of assets such as property, or stocks. This tax is due for the tax year in which the asset is sold.
There are two types of capital gains which are subject to tax. Long term capital gains tax is levied on those assets or investments that have been held for more than a year.
The current rates for long term capital gains tax are 0%, 15% or 20%, but this depends on the filer’s income. The income brackets are updated every year.
Short term capital gains tax is levied against profit made on investments or assets held for less than a year.
The rate of the short term capital gains tax is based on the taxpayer’s ordinary income bracket. For most people this is a higher tax than long term capital gains tax. There is a financial incentive to hold assets for more than a year in order to lower the capital gains tax.
The profit on an asset that is sold after less than a year is treated as earned income for tax purposes.
When an asset is sold the profit or capital gains is said to have been ‘realized’. The asset itself does not attract tax as long as it is unsold, regardless of how long it has been held.
Also read: Are Moving Expenses Tax Deductible?
Estate Tax
Estate tax is applicable when someone dies and their property or other assets are inherited by another person. This person may then be liable for estate tax.
However, the threshold for paying federal estate tax is over $12 million, so the vast majority of people will never have to pay this. Surviving spouses or descendants of the deceased who inherit don’t have to pay this levy either regardless of the value of the estate.
Although the threshold at which federal estate tax is set is high there are other state taxes which may be imposed. Estate tax is also known as death tax and more than a dozen states do levy it. Inheritance tax is imposed by six states.
The thresholds for these state taxes are lower than the federal estate tax, so more people may be liable for them.
State and federal estate taxes are based on the fair market value (FMV) of an estate. This may not be the same as the deceased paid for the property.
Any appreciation in value will therefore be taxed, but equally something bought at peak value which has then dropped will be taxed at the lower price.
Taxpayers can set up trusts for the transfer of wealth and to minimize estate taxes.
Also read: Are Home Improvements Tax Deductible?

Final Thoughts
There are many different types of taxes, but these four are the most common that income earners will be faced with in the United States.
We hope this guide to the main types of tax has helped you to understand how these levies work.
Our pay stub generator allows you to create pay stubs in a simple and easy-to-use manner.