Tax Tips for 1099 Workers: How To Reduce Your Tax Bill
As a self-employed person, you have a legal obligation to pay self-employment tax when your net earnings from your business income hit $400. This self-employment tax is 15.3% of your net profit, covering Social Security and Medicare.
Not exciting, right? If you are one of the roughly 16 million Americans who are self-employed, we have some tax tips for 1099 individuals on reducing your tax liability.
One of the best tax tips for 1099 workers is to understand how to reduce 1099 taxes. The good news is you're entitled to certain tax breaks. The 1099 IRS tax form presents information about your earnings. It could be about your sole proprietorship business, independent contractor jobs, or other miscellaneous income.
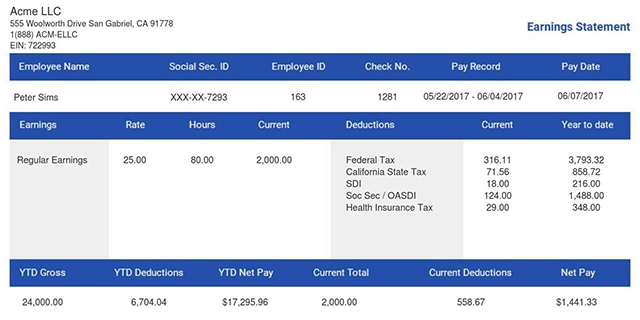
As such, you need to record your business income and expenses for your taxes. In this case, you need your pay stub. You can use a stub generator as an easy method to create it.
Read on to find out the details and discover how to lower 1099 taxes effectively.
Tax Tips for 1099 Workers: How To Reduce Self-Employment Taxes on 1099 Income
Here's how to lower 1099 taxes for independent contractors and self-employed individuals:
1. Have a Record of Your Business Income and Expenses
This is one of the most important 1099 tax tips. When you're an employee, your employer keeps a record of your gross income. So, it's easy to know how much you earned in a specific tax year. However, when you're self-employed or a small business owner, you have to track your earnings and business expenses. This means keeping every paid invoice and tracking all deductible business expenses. Although it’s not required, you may need to create a paystub for every paid job. It helps you track income and document records for tax purposes.
It's easy once you have a record of all your payments and business receipts for the year. You'll be able to calculate your gross income, and consequently your taxable income. If you don't know how to handle your business income, you won't be able to identify your tax bracket. This puts you at risk of underpaying or overpaying your income taxes.
2. Track All Deductible Business Expenses
Maximizing your business expense write-offs is key on how to reduce taxes on 1099 income. Many business expenses are tax-deductible from your income taxes. They include common tax deductions such as:
-
Advertising expenses and marketing costs
-
Business insurance
-
Car expenses related to your business. Examples include fueling to deliver a package to a client
-
Office supplies and expenses. Examples include cleaning services and stationery
-
Home office expenses. Examples include utility bills
-
Business travel expenses. Examples include buying an air ticket to attend a conference.
-
Legal fees and professional services
Ensure you always have business receipts for every tax-deductible business expense. When it's tax time, you'll simply sum up the business expenses. Then, file them as tax deductions on your Schedule C to lower your net profit and overall tax liability.
3. Use Tax Deductible Personal Expenses
Self-employment taxes treat you as both an employer and employee. You pay both the employer and employee portions of Social Security and Medicare. Therefore, you can deduct your qualified business and certain personal expenses. In the personal expenses category, you can deduct health insurance premiums. This includes premiums for you, your spouse, and your kids. This is a really useful tax deduction for self-employed individuals and small business owners.
4. Optimize Your Business Structure for Tax Savings
This is also an effective strategy on how to save taxes on 1099 income. Most self-employed people or those who own businesses form sole proprietorships. Sole proprietorships are easy and cheap to form. When your net income is high, this business structure may not be the best for self-employment tax savings. Consider forming an S corporation to enjoy substantial tax savings. This is generally beneficial once your net income exceeds roughly $60,000–$80,000, though you should consult a tax professional
An S corporation can help you minimize self-employment taxes. It allows you to pay yourself a portion of the profit taken as distributions. They are not subject to self-employment taxes. Also, it’s important to know your business tax due dates so you know when you have to file.
5. Consult a Tax Professional for 1099 Tax Tips

It can be sometimes difficult to know all your tax obligations while trying to earn a self-employment income. So, it's better to let a tax professional do this task for you. You'll pay for the service, but you'll likely make more tax savings. The professional will ensure you're making the most of all your deductions and any tax write-off. They'll give you personal tax tips for 1099 workers that fit your structure. They can also help you understand your estimated taxes and quarterly taxes. This ensures that you don't have to pay taxes in the form of penalties. Ensure they have all the IRS tax preparer requirements.
You may need a simple way to record individual payments, and the 123 paystub process can help to do so. Through this method, you can create your paystub in a few steps and download it.
Final Thoughts
Paying your income taxes is one of the most patriotic things you can do. However, that doesn't mean paying as much as possible. Tax deductions exist for a reason, and you should make good use of them to lower your tax bill. Lastly, learning how to reduce self-employment tax isn't a one-day thing. It takes some time to understand all the relevant provisions of the tax code.
If you need to generate any of your self-employed tax forms, you can create 1099 forms with us today. If you're also looking to create your pay documents, like your pay stub, use our paystubs creator. Get started with us today!